Website Semantic Core: What It Is and How to Build It Correctly
In this article, we explain what a website semantic core is, why it’s important, how to collect it, and how to use it to increase traffic and leads.
What Is a Website Semantic Core and Why You Can’t Start SEO Without It
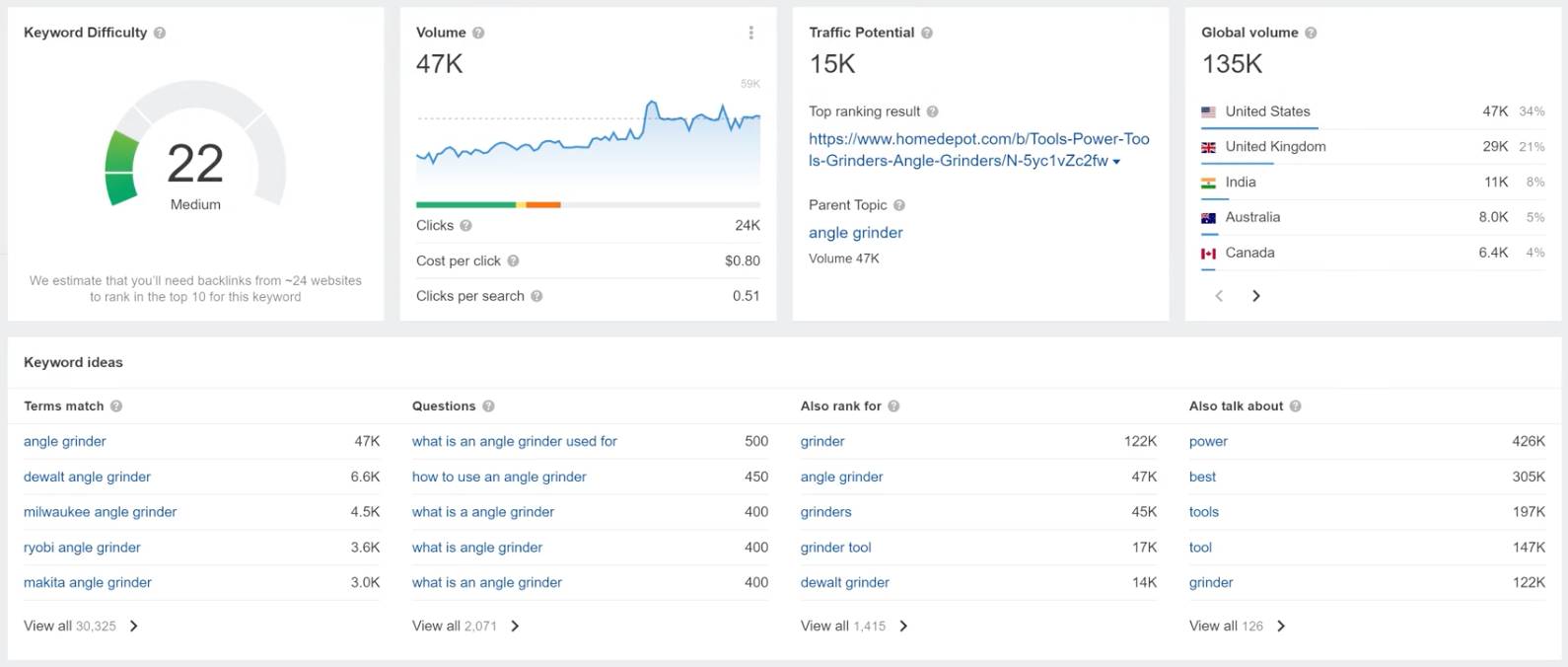
A semantic core (SC) is a structured set of keywords and phrases that users enter into search engines when looking for your products or services. Essentially, it is a comprehensive list of all possible query formulations reflecting demand in your niche.
For example, for an online clothing store, the semantic core would include queries like “buy dress,” “summer dresses,” “red dress cheap,” “women’s suits wholesale,” and hundreds of other variations. Each phrase represents a specific audience need.
Without a semantic core, a website risks promoting “blindly,” creating content at random without targeting real search queries. This leads to low traffic, wasted advertising costs, and lack of sales.
Why You Need a Semantic Core: Key Business Benefits
- Structuring the website. The SC helps design logical navigation: sections, categories, filters.
- Increasing organic traffic. The site covers more search queries and gets more visits.
- Focusing on target customers. Keywords show what users are searching for and help write content in their language.
- Reducing advertising costs. Semantic data is used in Google Ads – precise keyword selection = lower CPC.
- Improving conversion. A well-structured core attracts users who are ready to purchase.
Steps to Collect and Process a Website Semantic Core
Step 1. Niche and Competitor Analysis
First, define main business directions and audience segments. Then analyze competitors: which queries they rank for, site structure, and which pages bring traffic. Tools like Serpstat, Ahrefs, Semrush, and SimilarWeb are used.
Step 2. Keyword Collection
Tools used: Google Keyword Planner, Serpstat Keyword Research, Google suggestions, and “Related searches.” The goal is to collect the broadest list of real user search phrases.
Step 3. Filtering Out Irrelevant Keywords
Remove non-targeted queries, overly general terms (“website”), geo-mismatched queries (“in New York” if business is in Spain), and commercially irrelevant phrases.
Step 4. Clustering (Grouping)
Keywords are grouped by meaning. For example, “buy dress,” “cheap dress,” “women’s dress online store” form one group. Each group corresponds to a separate website page.
Step 5. Prioritization
Identify high-, medium-, and low-frequency queries. A combination of all levels ensures stable growth.
Step 6. Creating Website Structure
Based on keyword groups, build a sitemap: homepage, categories, subcategories, product pages, and informational blog. Avoid duplicating keywords and distribute them correctly across pages.
How to Use a Semantic Core in SEO Promotion
- When creating section and category structure.
- In H1–H3 headings and meta tags.
- In page content, product descriptions, and blog articles.
- In internal linking (anchors should match keywords).
- When setting up Google Ads campaigns.
- In analytics (traffic by keyword groups shows real effectiveness).
Important: Keywords should be used naturally. Content must be useful and readable. Over-optimization (keyword stuffing) harms SEO.
Tools for Keyword Research and Clustering
- Google Keyword Planner – basic statistics collection.
- Serpstat – competitor analysis, clustering, keywords.
- Ahrefs – evaluating query difficulty and competition.
- Key Collector – desktop solution for semantic work.
- Rush Analytics – clustering and group distribution.
Common Mistakes When Working with a Semantic Core
- Using only high-frequency keywords – high competition, slow results.
- Ignoring low-frequency queries – loss of target traffic.
- Failing to update the core regularly – semantics become outdated, demand changes.
- Duplicating keywords on multiple pages – self-competition.
- Keyword stuffing – ranking drop and search engine penalties.
Example of a Semantic Core Structure for an Online Store
- Category “Dresses”: buy dress, cheap dress, women’s dresses, summer dresses, office dresses.
- Subcategory “Evening Dresses”: buy evening dress, evening dresses online, red evening dress.
- Product Page: backless dress, black XS dress, buy Zara dress.
This distribution covers all levels of demand and drives traffic to specific pages.
Conclusion: Why SEO Doesn’t Work Without a Semantic Core
The semantic core is the map guiding your website toward target traffic and conversions. It defines structure, content, advertising, and analytics. Without it, work on the site becomes chaotic and ineffective.
Regular work with semantics is essential for long-term growth: the core should be updated every 6–12 months, considering new trends and user behavior.

 web-seo-ppc.com
web-seo-ppc.com
 web-seo-ppc.com
web-seo-ppc.com
 web-seo-ppc.com
web-seo-ppc.com web-seo-ppc.com
web-seo-ppc.com /web-seo-ppc.com
/web-seo-ppc.com https://web-seo-ppc.com
https://web-seo-ppc.com web-seo-ppc.com
web-seo-ppc.com

